CME matching algorithms explained

This guide is intended for traders, quants, and engineers who are working with CME Group products or building infrastructure that interfaces with futures and options markets. It’s especially relevant for those optimizing execution strategies or designing systems that interact directly with CME’s matching engine.
CME Globex operates as the electronic trading platform for CME, processing tens of millions of transactions daily. When an order is placed, it enters the order book where matching algorithms determine how it interacts with other orders. The matching algorithms that power this platform determine how incoming orders interact with resting limit orders.
Below are key matching algorithms used by the CME Group. Understanding these is essential for interpreting execution behavior, optimizing order placement, and building competitive trading systems.
Prioritizes orders that improve the market upon receipt. It can be combined with other matching algorithms like FIFO.
The minimum quantity an order must receive. Allocations below this threshold are disregarded or left unfilled.
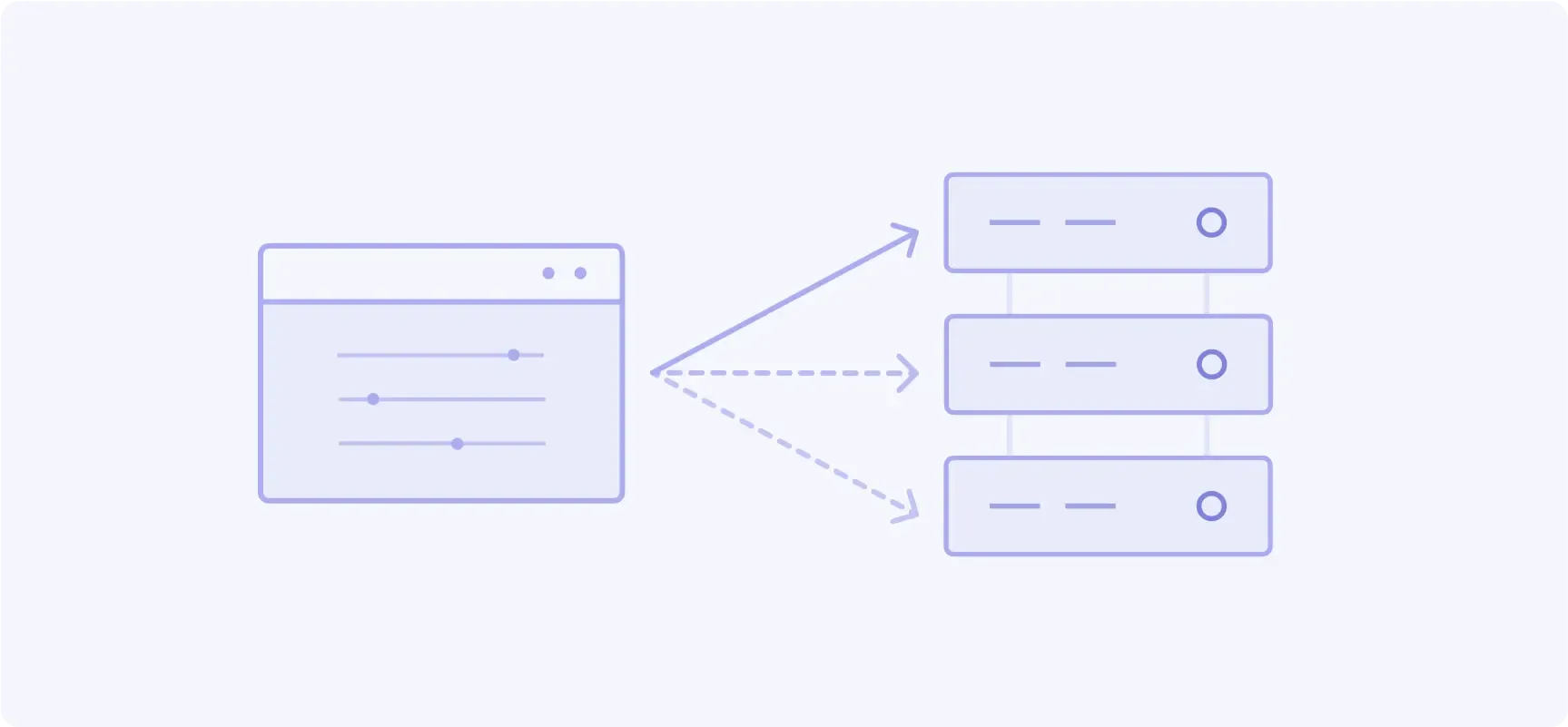
Aggressing orders match resting orders at the same price level by time priority until filled. Any residual quantity is left on the book.
- Popular products: ES, NQ, ZN, ZF, ZB, CL outrights
- Volume: 70.3%
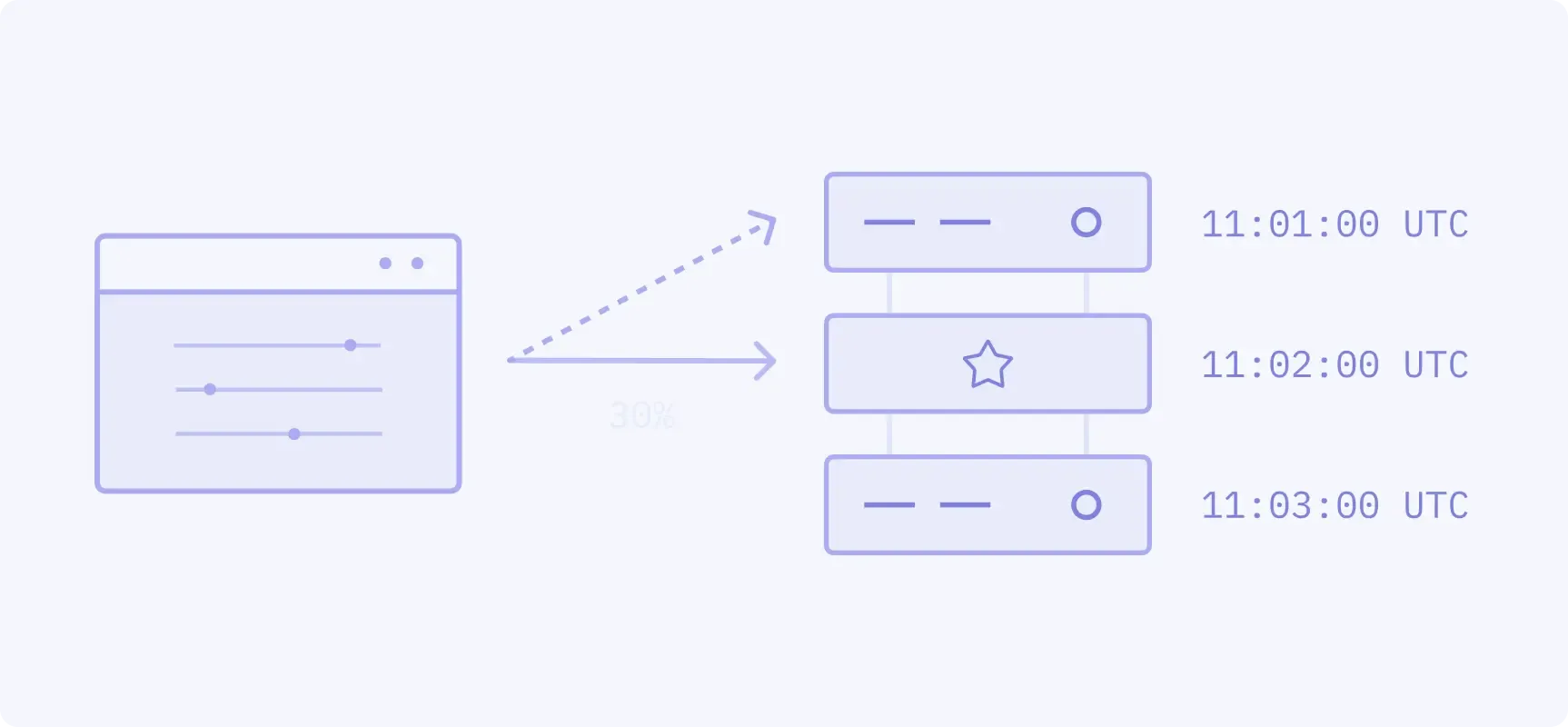
LMM orders are allocated a configurable percentage of an aggressor order before FIFO matching begins.
- Popular products: SR3 averaged price bundles
- Volume: 0.5%
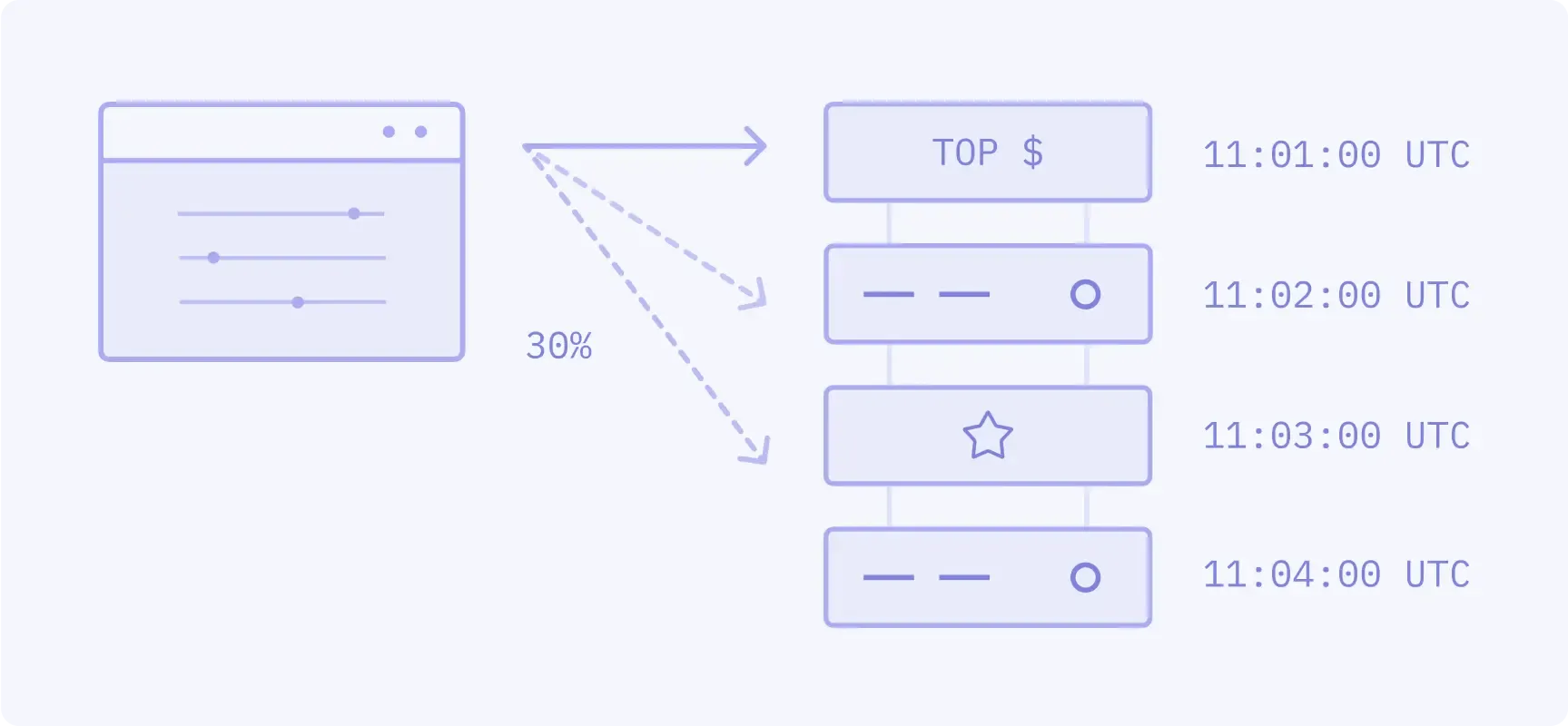
First order that improves the market is matched (top order), followed by LMM allocation and FIFO.
- Popular products: Not currently in use
An incoming aggressor order quantity is matched based on each resting order's pro-rated percentage. Allocations are rounded down to the nearest integer, including 0. Excess lots are allocated FIFO.
- Popular products: 6S, 6M calendar spreads
- Volume: <0.0001%
Divides quantity between FIFO and pro rata, according to product-specific parameters.
Any remaining quantity from rounding is distributed among participating orders, with no order receiving more than one lot.
Flexible algorithm with steps that can be turned on or off depending on product requirements.
- Popular CME products: ZT, ZQ, ZC, ZS, ZW outrights
- Volume: 12.7%
First assigns a top order percent allocation, followed by pro rata with a minimum allocation of two lots, followed by FIFO.
- Popular CME products: SR3 outrights
- Volume: 10.5%
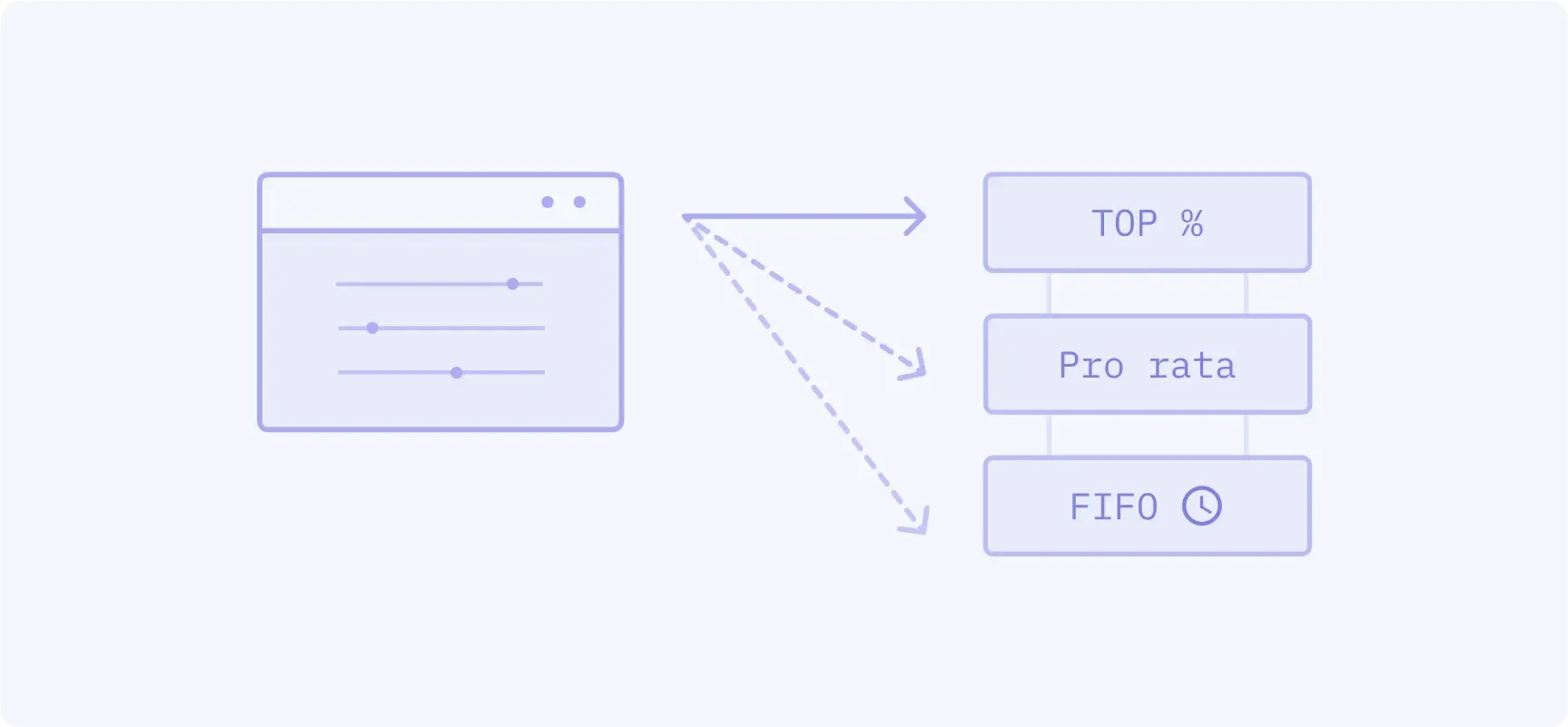
First assigns a top order percent allocation, followed by pro rata with configurable minimum allocation, followed by FIFO.
- Popular CME products: Corn options
- Volume: 1.4%
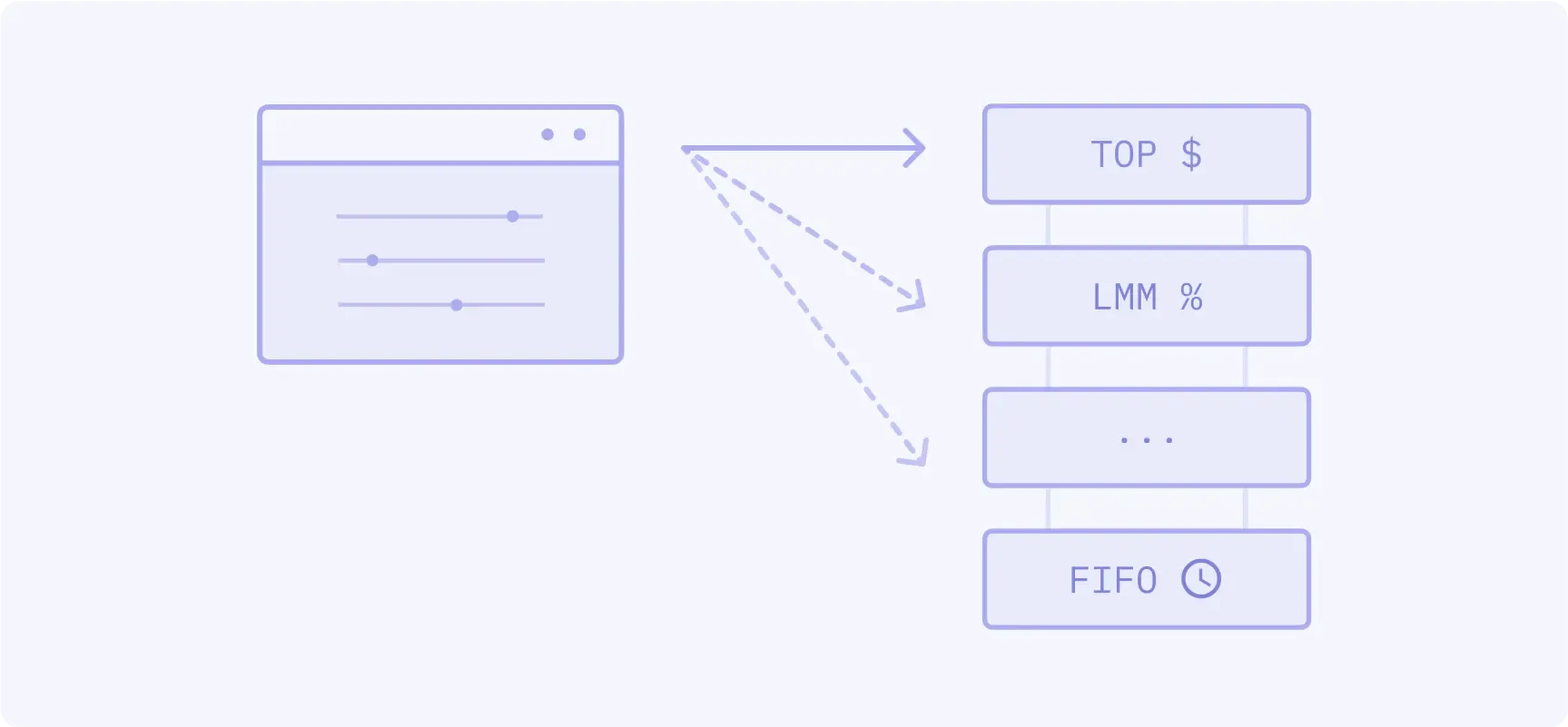
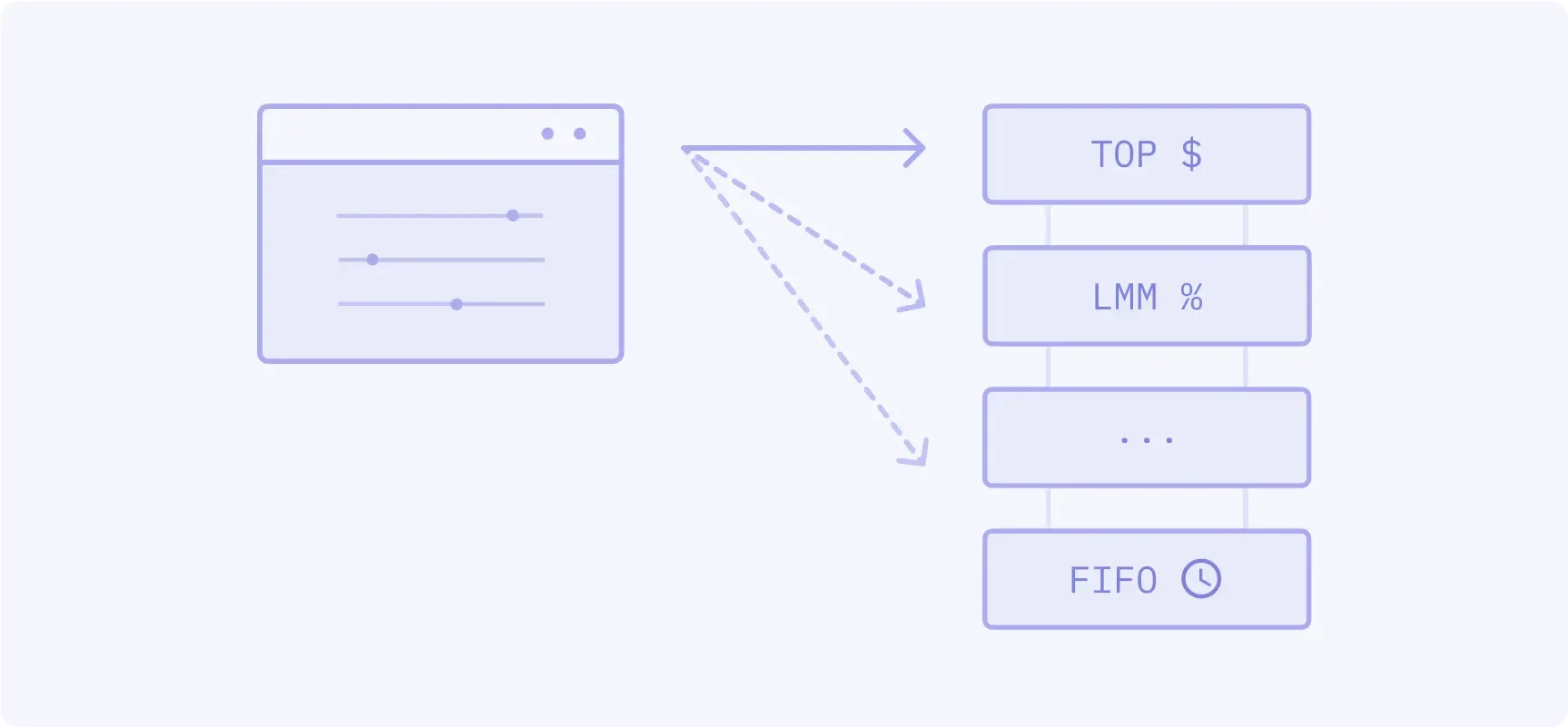
First assigns a top order percent allocation, followed by LMM allocation, followed by pro rata with configurable minimum allocation, followed by FIFO.
- Popular CME products: 10-Year T-note options
- Volume: 4.6%
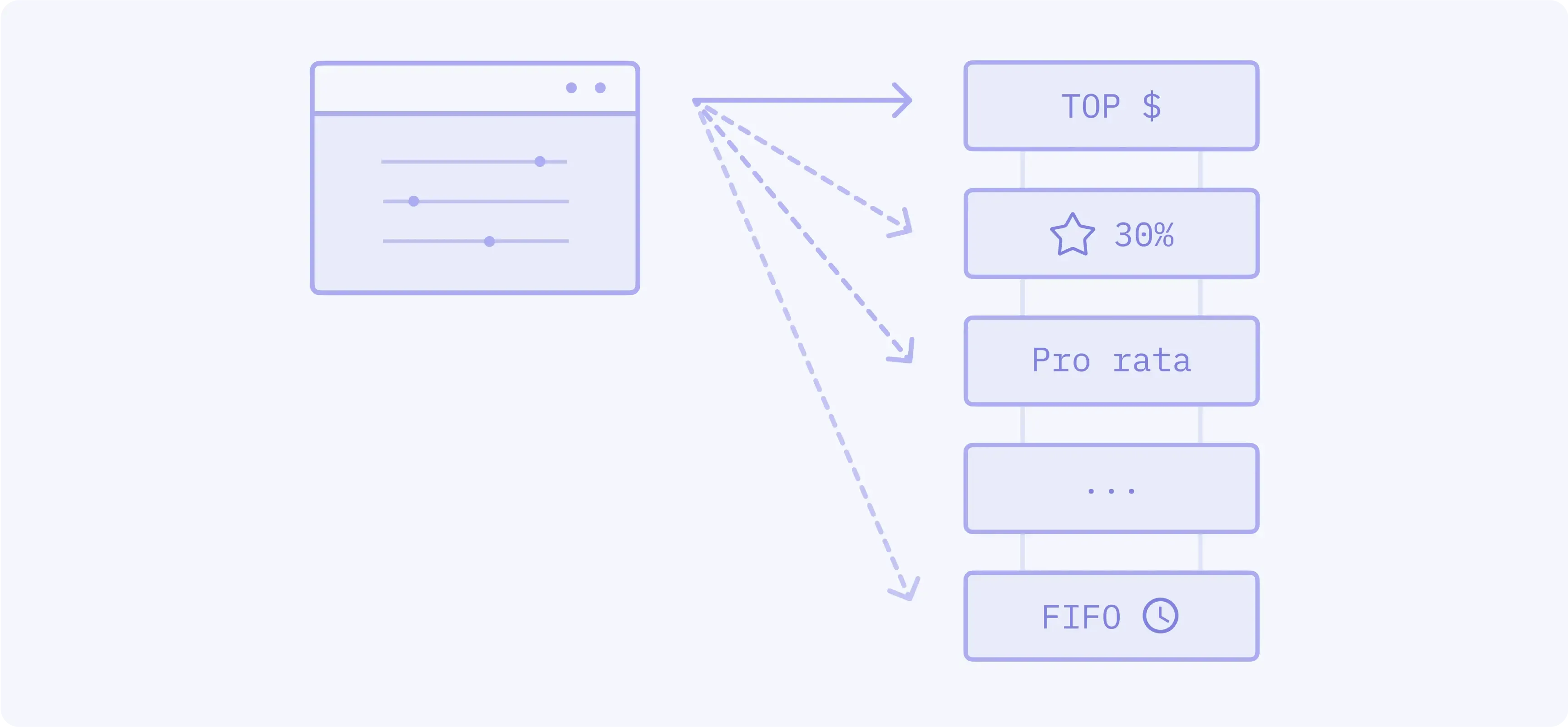
These matching algorithms are a part of the core infrastructure that processes billions of dollars in trading volume daily across CME markets. Each algorithm creates distinct execution characteristics that shape how orders interact. The variety of matching engines—from basic FIFO to complex threshold pro rata systems—represents how order matching systems adapt to different market structures and participant needs.